La Nina
Syllabus: GS1/Climatology
Context
- The forecast of above-normal rainfall coincides with the prediction of La Nina conditions developing later in the monsoon season. La Nina is known to bring increased rainfall to India, so these two factors together suggest a promising outlook for the monsoon.
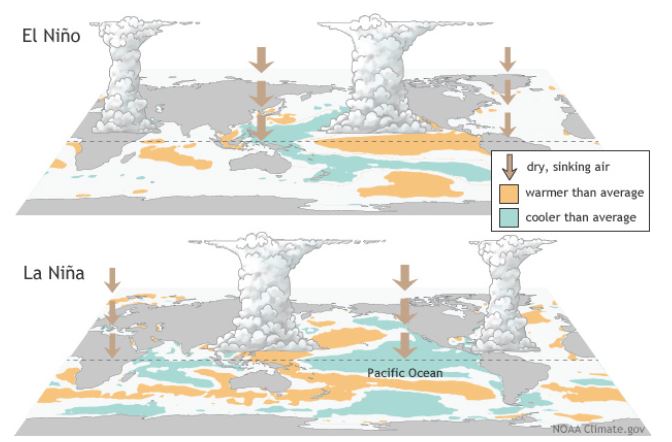
- La Nina cools the eastern Pacific Ocean, leading to stronger trade winds.
- Stronger trade winds push more warm water towards Indonesia, increasing rainfall there.
- This atmospheric circulation also helps strengthen the monsoon system, bringing more rain to India.
La Nina
- Meaning and Origin: El Nino, Spanish for “Little Boy,” refers to the warming of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- Cause: Weakened trade winds cause warm surface water to pile up near the Americas, pushing cooler water westward towards Asia.
La Nina and Its Impacts
- La Nina, which translates to “Little Girl” in Spanish, is a climate phenomenon characterized by cooler than average sea surface temperatures in the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean. It’s essentially the opposite of El Nino (“Little Boy”).
Impacts of La Nina:
- Increased Rainfall: La Nina brings above-average rainfall to Southeast Asia, northern Australia, and parts of South America. In India (except eastern and northeastern regions), La Nina is associated with normal or above-average monsoon rainfall.
- Drier Conditions: Conversely, La Nina can lead to drought conditions in some areas like the southwestern United States and parts of Africa.
- Stronger Atlantic Hurricanes: La Nina creates conditions favorable for hurricane development in the Atlantic.
- Cooler Temperatures: La Nina can bring cooler temperatures to the Pacific Northwest of the United States and parts of South America.
- Impact on India: El Nino events are often linked to below-average monsoon rainfall in India, leading to droughts with significant consequences for agriculture, water resources, and the economy.
- Additional Impacts: El Nino can also bring increased temperatures, higher risk of forest fires, water scarcity, and disruptions to fisheries in India.
Conclusion
- Climate Change and ENSO: Climate change, primarily caused by human activities, is expected to influence the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle.
- Increased El Nino Events: Studies suggest global warming may alter average ocean conditions in the Pacific, potentially leading to more frequent El Nino events.
- Impact on Extreme Weather: The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) warns that climate change could affect the intensity and frequency of extreme weather events associated with both El Nino and La Nina.

No Comments