Combating Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
Syllabus: GS2/Health
Why in news
- Recently, the Global Steering Group on Antimicrobial Resistance published a report highlighting the urgent need for action to combat antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Understanding AMR
- AMR (Antimicrobial Resistance) is a growing global health threat.
- It occurs when germs like bacteria, viruses, and fungi develop resistance to the drugs designed to kill them (antimicrobials like antibiotics, antifungals).
- This makes infections harder to treat, increasing the risk of complications, death, and healthcare costs.
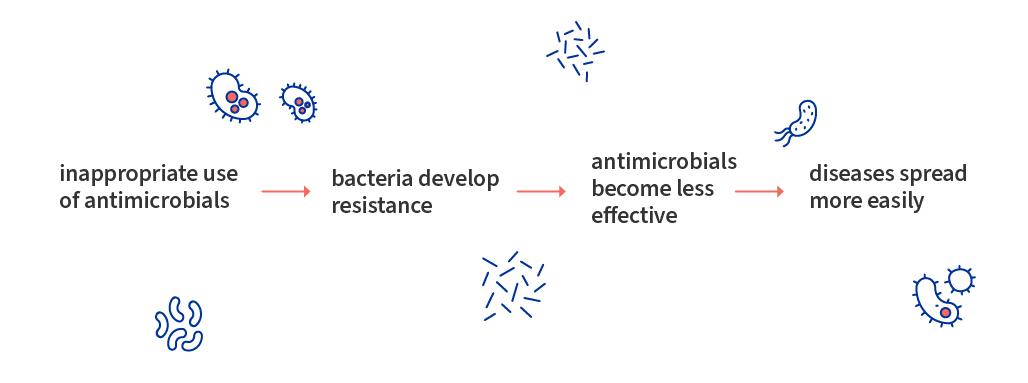
Causes of AMR
- Misuse and overuse: Overusing antibiotics in humans (e.g., for viral infections) and animals (e.g., for growth promotion) promotes resistance.
- Poor infection control: Practices like inadequate hand hygiene in hospitals can spread resistant germs.
- Agricultural practices: Routine use of antibiotics in livestock farming contributes significantly to AMR.
The Scale of the Problem
- AMR is already a leading cause of death globally, with millions of deaths annually, especially in low- and middle-income countries.
- It threatens the effectiveness of modern medicine, making routine procedures like surgery risky.
- AMR is projected to cause significant economic burden due to increased healthcare costs and lost productivity.
Combating AMR
- Prevention: Implementing proper hygiene, sanitation, and infection control measures are crucial.
- Antibiotic Stewardship: Promoting responsible use of antimicrobials in human and animal healthcare is essential.
- Surveillance: Establishing robust systems to track resistance patterns helps guide prevention strategies.
- Research and Development: Investing in new diagnostics, antibiotics, and vaccines is critical.
- Global Collaboration: A coordinated international effort is needed to address AMR effectively.
India Specific Initiatives
- National Action Plan on AMR (NAP-AMR): This plan adopts a “One Health” approach, involving various sectors like human health, animal health, and agriculture.
- AMR Surveillance and Research Network: Established by ICMR, it tracks resistance patterns in India.
- Antibiotic Stewardship Program (AMSP): A pilot program to promote responsible antibiotic use in hospitals.
Conclusion
- AMR is a complex problem requiring a multi-pronged approach. We need continued research and development alongside ensuring equitable access to existing and new solutions. Effective measures can save lives and money, making the fight against AMR a global priority.

No Comments