India and Nepal’s Border Issue
Syllabus: GS2/International Relations
Why in news
- Nepal printing a new Rs 100 note depicting disputed territories has brought the border issue back into focus.
About news
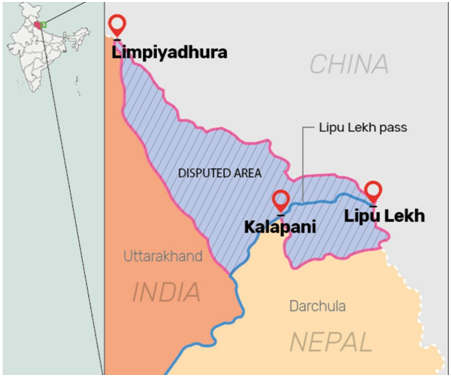
Area of Dispute:
- The disagreement centers around a 372-square-kilometer area encompassing Limpiyadhura, Lipulekh, and Kalapani near the India-Nepal-China trijunction.
Recent Developments:
- In 2019, India included the disputed territories in its official map.
- Nepal responded in 2020 by issuing a map claiming the same region.
Basis for Claims:
- Nepal: Relies on the Sugauli Treaty of 1816, which designated the Kali River as the western boundary. Nepal interprets the source of the river (eastward limit) to be near Limpiyadhura.
- India: Contends the border starts at Kalapani, where the river emerges from the mountains.
Susta Border Dispute:
- Susta, a territory claimed by both Nepal and India, is currently administered by India’s West Champaran district.
- Nepal asserts ownership of over 14,860 hectares they believe India has encroached upon.
India-Nepal Relations:
Despite the Susta dispute, India and Nepal share a close and multifaceted relationship:
- Historical and Cultural Bonds: The “roti-beti” relationship signifies cultural exchange and cross-border marriages.
- Geographical Interdependence: Nepal, landlocked, relies heavily on India for trade and access to the sea.
- Treaty and Open Border: The 1950 Treaty of Peace and Friendship forms the foundation of their special relationship, granting Nepalese citizens opportunities similar to Indians.
- Defense Cooperation: India assists Nepal’s military with training and equipment, and Gurkha regiments from Nepal serve in the Indian Army.
- Infrastructure and Development: India supports Nepal’s development through road upgrades, cross-border rail links, and integrated check posts.
- Energy Cooperation: Power exchange agreements ensure energy needs are met in border regions.
- Trade and Economy: India is Nepal’s largest trading partner, with significant growth in bilateral trade. India is a major source of exports for Nepal.
- Recent Developments: A motorable bridge across the Mahakali River is being constructed with Indian assistance.
- Disaster Relief: India provided substantial aid following the 2015 Nepal earthquake (Operation Maitri).
Issues Straining India-Nepal Relations
- Treaty of Peace and Friendship (1950): While intended to strengthen ties, Nepal now views the treaty as unequal and potentially limiting its sovereignty.
- Madhesi Issue (2015): Blockades at the border erupted due to protests by the Madhesi people, who felt marginalized by Nepal’s new constitution. This strained relations with India, seen as supportive of the government.
- Chinese Influence: China’s growing economic and infrastructure involvement in Nepal, through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative, is perceived by India as a strategic threat and a challenge to its traditional dominance in the region.
- Security Concerns: The porous India-Nepal border facilitates smuggling and movement of potentially dangerous individuals, posing a security risk for India.
Way forward
Importance of a Strong Relationship:
- Shared History and Culture: Deep cultural connections provide a strong foundation.
- Strategic and Economic Benefits: Nepal serves as a buffer against China and is an important economic partner.
Resolving Border Disputes:
- Lessons from India-Bangladesh: The successful resolution of their land border dispute offers a valuable model.
- Explore Realistic Solutions: Both sides need to be willing to compromise and find mutually agreeable solutions.
Possible Strategies:
- Renewed Dialogue: Open and frequent communication between leaders is crucial.
- Address Madhesi Concerns: Finding a solution that addresses the grievances of the Madhesi population is vital for stability.
- Cooperation on Security: Collaborating on border management and intelligence sharing can enhance security for both nations.
- Infrastructure Development: Joint infrastructure projects can foster economic interdependence and mutual benefit.
Conclusion:
- By acknowledging the historical and strategic significance of their relationship, India and Nepal can work together to address current issues and build a more stable and prosperous future

No Comments