Carbon Farming
Syllabus: GS3/Environment/Agriculture
why in news
- Techniques within carbon farming can reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
About
- Carbon farming, also known as carbon sequestration farming or regenerative agriculture, refers to a set of agricultural practices designed to capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in the soil or biomass. The goal is to mitigate climate change by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
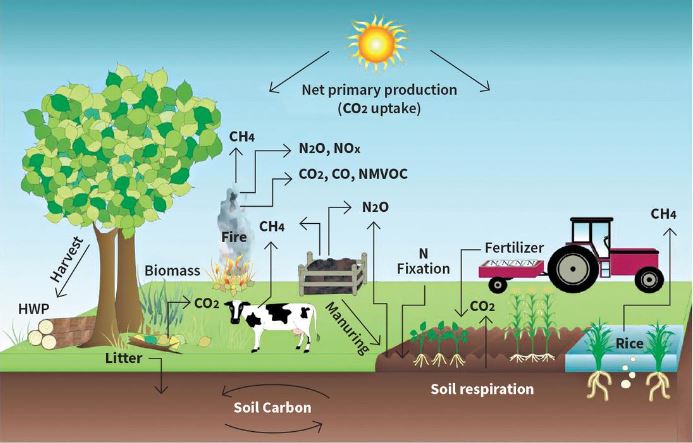
Techniques
There are several techniques that can be used in carbon farming, including:
- Reduced tillage: This practice minimizes the disturbance of the soil, which helps to keep existing carbon stores intact and promote the growth of new plant roots that capture carbon.
- Cover cropping: Planting cover crops between cash crops helps to protect the soil from erosion, improve soil fertility, and sequester carbon.
- Composting and mulching: Adding compost and mulch to the soil helps to improve soil health and fertility, and also helps to retain moisture, which can promote plant growth and carbon sequestration.
- Biochar: Biochar is a charcoal-like substance that can be added to soil to improve fertility and water retention. It can also help to sequester carbon in the soil.
- Silvopasture: This practice integrates trees, shrubs, and forage crops into grazing land. The trees and shrubs help to sequester carbon, while also providing shade and shelter for livestock.
Common Techniques used in Carbon Farming
Carbon farming utilizes a variety of techniques to capture atmospheric carbon dioxide and store it in the soil or biomass.
- Cover cropping: Planting cover crops like legumes or grasses during fallow periods helps to protect and enrich the soil, promoting carbon storage.
- No-till farming:Avoiding or minimizing tillage helps to preserve soil structure and organic matter, preventing carbon loss from the soil.
- Agroforestry:Integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes not only sequesters carbon but also provides additional ecosystem services such as shade, windbreaks, and habitat for wildlife.
- Biochar:Biochar is a type of charcoal produced from organic materials like agricultural waste. When added to soil, biochar can enhance fertility and carbon sequestration.
- Perennial crops:Planting perennial crops instead of annuals helps to minimize soil disturbance and increase carbon storage over time. Examples of perennial crops include fruit trees, nut trees, and certain grasses.
- Integrated nutrient management practices promote soil fertility and reduce emissions by using organic fertilizers and compost.
- Livestock management strategies including rotational grazing, optimising feed quality, and managing animal waste can reduce methane emissions and increase the amount of carbon stored away in pasture lands.
Significance of Carbon Farming
- Climate Change Mitigation: By increasing carbon storage in agricultural lands, carbon farming acts as a natural carbon sink. This captured carbon is removed from the atmosphere, reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases and mitigating climate change.
- Soil Health Improvement: Many carbon farming practices, like cover cropping, crop rotation, and no-till farming, go hand-in-hand with improved soil health and fertility. These practices promote the growth of beneficial soil microbes, improve soil structure, and increase organic matter content. Healthy soil leads to better water retention, reduced erosion, and ultimately, increased crop yields.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Carbon farming methods often prioritize the preservation and restoration of natural habitats within agricultural landscapes. This can involve planting hedgerows, creating wildlife corridors, and promoting diverse cropping systems. These practices provide crucial habitat for native species, support pollinators like bees and butterflies, and enhance overall biodiversity. A diverse ecosystem is more resilient to pests, diseases, and environmental changes.
- Resilience to Climate Change: Climate-resilient agriculture practices, such as agroforestry and diversified cropping systems, are often promoted within carbon farming. These practices can help farmers adapt to the impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events, droughts, and floods. For example, agroforestry systems with deep-rooted trees can help improve drought tolerance and provide shade for crops and livestock.
Opportunities for Carbon Farming in India
India has a significant opportunity to leverage carbon farming for both environmental and economic benefits.
- Agro-Ecological Practices: Existing grassroots initiatives and research in organic farming demonstrate the potential for carbon sequestration. Large-scale adoption of these agro-ecological practices across India’s estimated 170 million hectares of arable land could yield significant economic benefits, valued at around $63 billion.
- Financial Incentives: Carbon credit systems can incentivize farmers by providing additional income for adopting sustainable practices that provide climate services. Studies suggest agricultural soils have the potential to absorb 3-8 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent annually over 20-30 years. This carbon sequestration capacity could significantly contribute to mitigating climate change.
- Suitable Land: Regions with extensive agricultural land, like the Indo-Gangetic plains and the Deccan Plateau, are well-suited for carbon farming practices.
Challenges to Consider
- Dependence on Various Factors: The effectiveness of carbon farming varies depending on factors like location, soil type, crops grown, water availability, existing biodiversity, and farm size. Limited water availability, especially in hot and dry areas, can hinder plant growth and carbon sequestration through photosynthesis. Selecting the right plants is crucial, as fast-growing trees and deep-rooted perennial grasses are better at carbon storage but may not thrive in arid environments.
- Financial Assistance: Small-scale farmers, particularly in developing countries like India, often lack the resources to invest in sustainable land management practices and implementing carbon farming techniques. Financial assistance is needed to overcome these initial costs.
Conclusion: Scaling Up Carbon Farming in India
India has the potential to be a leader in carbon farming, but scaling up these practices requires addressing several challenges:
- Limited Awareness: Many farmers are unaware of carbon farming techniques and their benefits.
- Inadequate Policy Support: Government policies need to better incentivize and support the adoption of carbon farming practices.
- Technological Barriers: There may be a lack of access to technologies or knowledge required for certain carbon farming practices, such as composting or biochar production.
- Enabling Adoption Environment: Creating an environment that encourages farmers to adopt carbon farming, such as by simplifying certification processes or providing technical assistance, is crucial.
Despite these challenges, promoting carbon farming is in India’s best interest. It offers a strategy to:
- Mitigate climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide.
- Improve soil health and fertility, leading to increased crop yields.
- Enhance biodiversity within agricultural landscapes.
- Create economic opportunities for farmers through carbon credits and potentially higher yields.

No Comments