The First Indian Human Spaceflight ”Gaganyaan”
UPSC Relevance
- Science and Technology: India’s space exploration capabilities, significance of Gaganyaan mission.
- Mains GS III: Indigenization in strategic sectors like space.
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently announced the final shortlist of candidates selected to be astronauts aboard Gaganyaan, the first human spaceflight mission by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
Key Points:
- Gaganyaan is a crucial mission for India, aiming to demonstrate its indigenous human spaceflight capability.
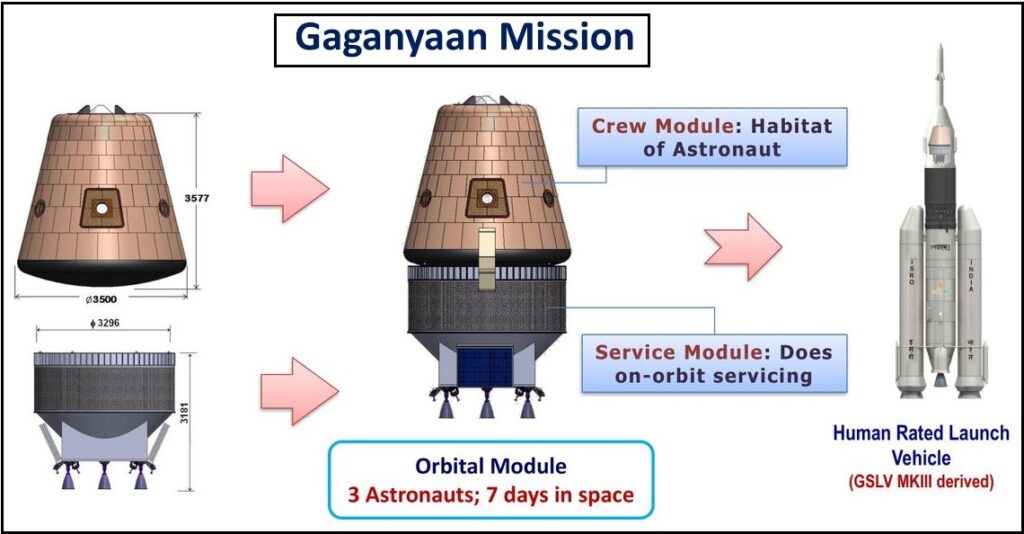
- The mission plans to send a three-member crew to a low Earth orbit (LEO) at an altitude of around 400 km for a period of up to seven days.
- This shortlist announcement signifies a significant step forward in finalizing the crew for this historic mission.
Introduction
- India’s ambitious Gaganyaan mission signifies a crucial leap into human spaceflight, aiming to place the nation amongst the elite group capable of undertaking independent space exploration with astronauts.
Key Points
1. Objective
Demonstrate indigenous human spaceflight capability by sending a crew to a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) for three days and ensuring their safe return.
2. Mission Design
Three missions: Two unmanned and one manned.
- Unmanned missions for technology demonstration before the crewed mission.
- Demonstration missions include Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT), Pad Abort Test (PAT), and Test Vehicle (TV) flights.
3. Launch Vehicle
Human-rated LVM-3 (HLVM-3), a reliable heavy-lift launcher with a Crew Escape System (CES) for emergencies.
4. Orbital Module
- Crew module: Habitable space with an Earth-like environment for the crew.
- Service module: Provides support to the crew module in orbit (propulsion, power, thermal systems).
- Features: Parachutes, Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLS), gynoid (robot) named Vyommitra for critical tasks.
5. Human Spaceflight Centre
Established in 2019, in Bangalore, for crew training and mission management.
Benefits
- Future Explorations: Paves the way for sustained human and robotic exploration of the solar system.
- Technological Advancement: Boosts capabilities for human space exploration, sample return missions, and scientific research.
- International Collaboration: Enables participation in global space station development and conducting scientific experiments.
- Job Creation: Generates employment opportunities in advanced scientific research and development.
- Scientific Temperament: Fosters scientific curiosity and inspires young minds towards STEM careers.
- Global Leadership: Strengthens international partnerships and global security through peaceful space exploration.
Challenges
- Space Debris Management: Requires advanced tracking systems to avoid collisions with debris in LEO.
- Cabin Depressurization Risk: Robust spacecraft design with protective shielding is crucial.
- Complexity of Replicating Earth-like Conditions: Maintaining a suitable environment in a confined space presents challenges.
- Resource Management: Lightweight and efficient life support systems, food production, and waste recycling are essential.
- Technological Innovation: Continuous development is needed for reliable, compact, and energy-efficient systems to sustain human life in space.
Future Outlook
Gaganyaan is a stepping stone towards India’s vision of an indigenous space station by 2035 and a potential lunar landing by 2040. The mission signifies India’s growing self-sufficiency in space exploration.
Possible Questions
- Discuss the significance of Gaganyaan mission for India’s space program.
- Critically analyze the challenges and opportunities associated with India’s human spaceflight program.
- How can India leverage its space exploration capabilities for socio-economic development?
SOURCE

No Comments